- Introduction
- Malware group History
- Analysis of BloodAlchemy
- The code similarities with Deed RAT
- Summary
- Appendix
This post is also available in: 日本語
Introduction
This article examines the analysis of a malware called "BloodAlchemy" that we observed in an attack campaign.
In October 2023, BloodAlchemy was named by Elastic Security Lab 1 as a new RAT (Remote Access Trojan). However, our investigation has revealed that BloodAlchemy is not an entirely new malware but an evolved version of Deed RAT, the successor to ShadowPad.
Malware group History
Let's look at ShadowPad first. ShadowPad is a particularly notorious malware family used in APT (Advanced Persistent Threat) campaigns. It was first reported in a software supply chain attack in July 2017. At that time, ShadowPad was embedded in one of the code libraries of a server management software for enterprise networks provided by NetSarang 2.
In the early stages of 2019, it was believed that only APT41 was using ShadowPad. However, since 2020, many security researchers reported that it may have been utilized by various APT groups 3.
Moving on to Deed RAT, it is believed to have been used as a RAT by the threat group called Space Pirates, active since at least 2017, based on its implementation. Additionally, Positive Technologies’ security team suggests that Deed RAT shows a high degree of code similarity with ShadowPad4.
Now, let's delve into BloodAlchemy, the malware in question. According to Elastic Security Lab’s analysis, this malware exhibits several characteristics, such as using legitimate binaries to load malicious DLLs, multiple run modes, persistence mechanisms, and importing specific functions of various communication protocols when communicating with its command and control (C2) server. These traits indicate that BloodAlchemy is a new variant of Deed RAT that is still being actively developed by attackers.
The public information of ShadowPad, Deed RAT, and BloodAlchemy is as follows:

References of Figure 1
[1] ShadowPad in corporate networks
[2] Operation ShadowHammer: a high-profile supply chain attack
[3] Cyber Espionage Tradecraft in the Real World Adversaries targeting Japan in the second half of 2019
[4] Space Pirates: analyzing the tools and connections of a new hacker group
[5] ShadowPad: the Masterpiece of Privately Sold Malware in Chinese Espionage
[6] Operation StealthyTrident: corporate software under attack
[7] APT Threat Landscape in Japan 2020
[8] RedHotel: A Prolific, Chinese State-Sponsored Group Operating at a Global Scale
[10] Attacks on industrial control systems using ShadowPad
[11] Redfly: Espionage Actors Continue to Target Critical Infrastructure
[12] Space Pirates: a look into the group's unconventional techniques, new attack vectors, and tools
Analysis of BloodAlchemy
Initial infection vector and infection flow
In this case, we analyzed that the attacker used a file set to infect targets with BloodAlchemy by taking over a vender-use-only maintenance account on a VPN device. Figure 2 shows the infection flow.

The malicious file set consisted of three files: BrDifxapi.exe, BrLogAPI.dll, and DIFX. These files were stored under the directory C:\windows\. Additionally, a scheduled task (C:\Windows\System32\Tasks\Dell\BrDifxapi) was created for persistence.

Analysis of malicious DLL
When BrDifxapi.exe is executed on the infected host, it leverages the DLL side-loading technique to load a malicious DLL file called BrLogAPI.dll in the same directory.
Subsequently, this malicious DLL loads the DIFX file and decrypts shellcode from it, executing the shellcode in memory. The crypto algorithm is AES128 (CBC mode), and the key is the first 16 bytes of the DIFX file.


Analysis of shellcode
The decrypted shellcode contains an encrypted and compressed form of BloodAlchemy. This custom decryption process based on the FNV-1a hash algorithm and the lznt1 compression.
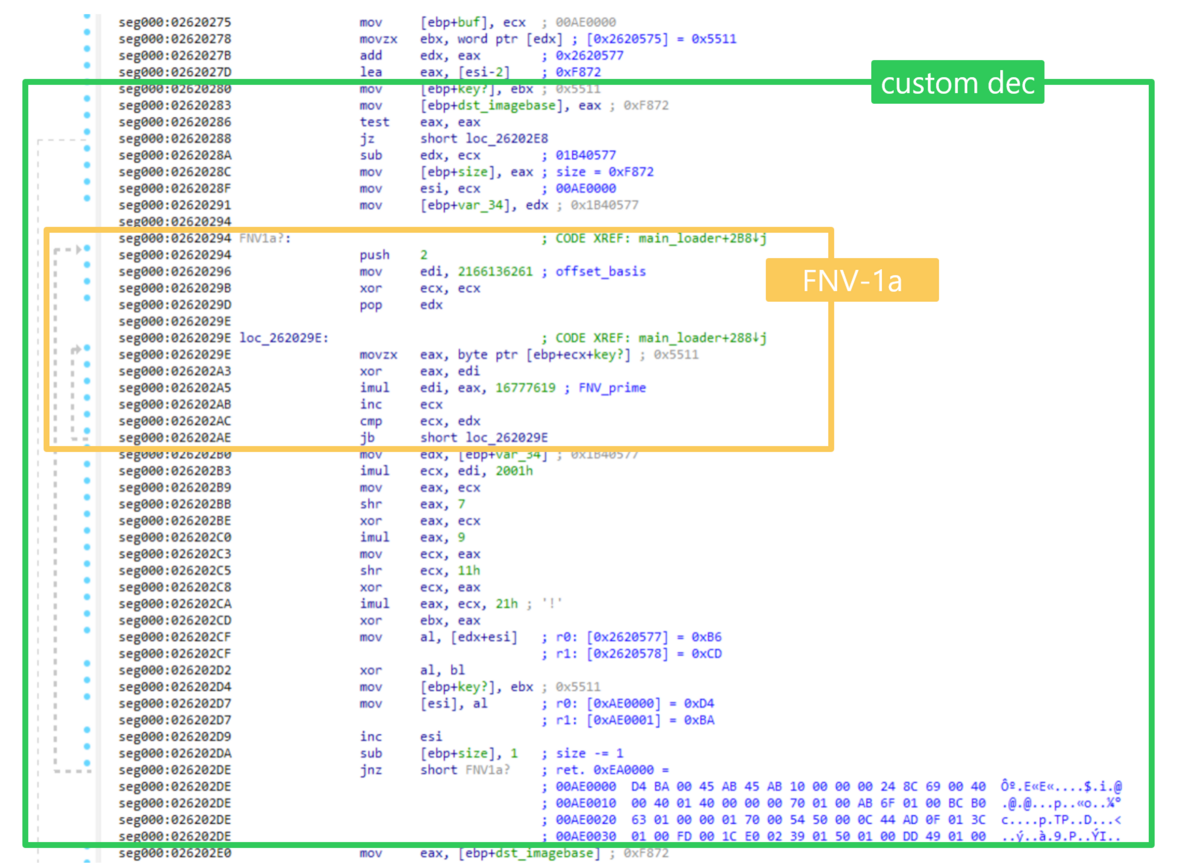
What is FNV-1a hash algorithm?
Fowler-Noll-Vo (FNV) is a hash algorithm based on an idea originally submitted as reviewer comments to the IEEE POSIX P1003.2 committee by Glenn Fowler and Phong Vo in 1991. It was later improved by Noll. > FNV is an abbreviation that combines the names of its creators. FNV is widely used for various purposes, including DNS servers, X (formerly Twitter) services, database index hashing, major web search/index engines, Message-ID search functionality in netnews history files, and > spam filtering, among others.

What is LZNT1 compression algorithm
The compression algorithm that can be easily used by calling the Windows API named RtlDecompressBuffer.
It has been discovered that the restored BloodAlchemy payload has a unique data format that closely resembles the PE format but is different. Below are the data structures of the custom format.
| offset | Descriptions | Data |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | magic number | 45 AB 45 AB |
| 0x04 | plugin id | 0x10 |
| 0x08 | entry point | 0x698c |
| 0x0c | original base | 0x400000 |
| 0x10 | absolute offset | 0 |
| 0x14 | size of virtualalloc | 0x17000 |
| 0x18 | size of raw data | 0x16fab |
| 0x1c | size of unknown | 0x163bc |
| 0x20 | base of code? | 0x1000 |
| 0x24 | section1: virtual address | 0x0 |
| 0x28 | section1: raw data address | 0x50 |
| 0x2c | section1: size of raw data | 0x10fa0 |
| 0x30 | section2: virtual address | 0x11000 |
| 0x34 | etc.. |
Once the BloodAlchemy payload is restored, the previous mentioned shellcode interprets this custom format for deploying the final payload into memory and executes it as the fireless malware (Figure 8).

Analysis of payload (BloodAlchemy)
Structures
BloodAlchemy has several features that are not commonly found in other malware. One of these features is the 'run mode' value. When transferring the processing from the shellcode mentioned earlier to the entry point of the payload, it is called with six specified arguments.
The first argument set the value of run mode, and the BloodAlchemy's behavior varies significantly based on this value. The following table summarizes the values for each run mode and their corresponding behaviors:
| run mode | Behavior corresponding to each run mode |
|---|---|
| 0 | Communication with C2 and backdoor functionality, creation of specified process for code injection, code injection into specified processes, anti-debugging, anti-sandbox techniques, Persistence |
| 1 | Communication with C2 and backdoor functionality |
| 2 | Creation of thread for Communication with C2 and backdoor functionality |
| 3 | Communication with C2 and backdoor functionality, code injection into specified processes, anti-debugging, anti-sandbox techniques, Persistence |
| 4 | Creation of specified process for code injection |
| 5 | Creation of named pipes |
| 6 | Installation of malware |
It has been confirmed that BloodAlchemy exhibits the ability to load a malware configuration. This configuration is embedded in an encrypted state within the previous shellcode and, it is decrypted and utilized during BloodAlchemy’s execution (Figure 9).
Furthermore, if a file with a 15-character filename consisting of [a-zA-Z] exists within the directory C:\ProgramData\Store, it will be loaded as the malware configuration. The same decryption algorithm used in the previously mentioned payload was utilized for this decryption process.

The malware configuration contains important data related to malicious code processing. This data includes values to manipulate the behavior set in the run mode, the URL of the C2 server, process names specified for code injection, and more. Some important data such as a MUTEX value, C2 server, target process name etc., are primarily encrypted. Additionally, it also includes offset values indicating the positions of these encrypted data like ShadowPad.

Each of these encrypted data is stored in the following order: the size of the encrypted data, a byte key, and the encrypted data itself.
| offset | descriptions | data |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | size of data | 0x25 |
| 0x01 | a byte key | 0x41 |
| 0x02 | encrypted data | 1E 9D 09 19 7A D0 9D 9D … |
The decryption is performed using another custom algorithm with the stored key. We created a simple Python script to decrypt the encrypted data.
import struct def dec_cmt(offset): s = struct.unpack("B", ida_bytes.get_bytes(offset, 1))[0] data = ida_bytes.get_bytes(offset, s + 2) iv = data[1] enc = data[2:] dec = "" for i in range(s): dec += chr(iv ^ enc[i] & 0xFF) ku0 = iv << (i % 5 + 1) & 0xFF ku1 = iv >> (7 - i % 5) & 0xFF iv = (iv + (ku0 | ku1)) & 0xFF return dec[:-1]
As an example, the resolved offsets and decrypted data for each value in malware configuration using the Python script is as follows:

Not only malware configuration, but the same encryption is also used for other embedded data, such as important data related to some specific file paths. This Python script can also decrypt these data as well.

Functions
As mentioned above, BloodAlchemy behaves differently depending on the run mode and the values in the malware configuration. From this characteristic, we believe the BloodAlchemy is a rather unique sample. The main function of BloodAlchemy is communication with a C2 server and controlling the infected host through the implemented backdoor commands.
The individual functionalities implemented in BloodAlchemy are introduced here.
Persistence
The payload incorporates a persistence capability. If the run_mode is 0 or 3 and the execution file path is not for persistence, and if the persistence_flag (a value of 0x34 in the malware configuration) is not 0, the persistence method will be chosen based on the value of the persistence_flag from 1 to 4.
1: service + startup + taskschd (COM obj)
2: service
3: startup
4: taskschd (COM obj)

The persistence mechanism is designed for the malware set consisting of test.exe, BrLogAPI.dll, and DIFX to be created within one of the corresponding directories based on the infected environment.
- %AUTOPATH%\Test\
- %LocalAppData%\Programs\Test\
- %ProgramFiles%\Test\
- %ProgramFiles(x86)%\Test\
Anti Sandbox
The payload also has anti-sandbox capabilities to evade analysis in sandbox environments. This feature only functions when the run_mode is 0, the executable file path is not for persistence, and the value of 0x1c in the configuration is 1. It checks the process_name, files, and DNS results. It is speculated that the purpose of this feature is to avoid detection from Trellix sandbox functionality, based on the checked process names.

Process Injection
The process injection feature was implemented with following conditions which were the run_mode is 0 or 3 and the value of 0x54 in the configuration is 1, it attempts to inject the previous shellcode into the following processes specified in the configuration from 0x58 to 0x64.
- %windir%\system32\SearchIndexer.exe
- %windir%\system32\wininit.exe
- %windir%\system32\taskhost.exe
- %windir%\system32\svchost.exe
In order to set the injected shellcode as a queue for asynchronous procedure calls (APC), the QueueUserAPC() function is used. This technique is known as Early Bird Injection.
What is Asynchronous Procedure Call (APC)
A function that is executed asynchronously in the context of a specific thread. Each thread has its own APC queue, and an application can register an APC in the queue by calling the QueueUserAPC() function. This > will result in the execution of the APC function and the occurrence of a software interrupt during the next scheduled thread."

As related feature of the payload, if the run_mode is 0 or 4 and the value of 0x68 in the configuration is 1, it creates the following processes specified from 0x6c to 0x74 and attempts to inject the shellcode into those processes using QueueUserAPC() too.
- %windir%\system32\wininit.exe
- %windir%\system32\taskeng.exe
- %windir%\system32\taskhost.exe
- %windir%\system32\svchost.exe
Creation of VFT associated with each communication protocol
The BloodAlchemy was designed for up to 10 C2 destinations. However, interestingly, in the samples we observed, only one C2 information was in there. Based on the C2 information, the communication protocol is extracted, and the Protocol ID to be used within the malware is set. Based on this Protocol ID, the functions necessary for communication are imported, and a Virtual Function Tables (VFT) is created..
What is Virtual Function Tables (VFT)
A table that stores pointers to virtual functions within a class. If a class has one or more virtual functions, the compiler creates a virtual function table for that class. Each instance of the class holds pointers to this > table.

Backdoor commands
15 backdoor commands were implemented to control victim machine. The operations performed by each command ID are as follows:
| command id | descriptions |
|---|---|
| 0x1101 | update config |
| 0x1102 | get current config |
| 0x1201 | update test.exe |
| 0x1202 | update BrLogAPI.dll |
| 0x1203 | update DIFX |
| 0x1204 | uninstall and terminated |
| 0x1205 | launch persistence_dir\test.exe |
| 0x1301 | unknown |
| 0x1302 | load received payload and store it into registry value |
| 0x1303 | delete registry value |
| 0x1304 | unknown |
| 0x1401 | get proxy info |
| 0x1402 | update proxy info |
| 0x1501 | gather victim info |
| 0x1502 | echo 0x1502 |

The code similarities with Deed RAT
Based on our reversing results, we have discovered multiple similarities between BloodAlchemy and Deed RAT. Here are some examples of code similarities that we consider particularly significant:
The first remarkably similar point is the unique data structures of the payload header in both BloodAlchemy and Deed RAT. Although there are differences in values such as magic number and plugin ID and other values. This data structure is designed based on the PE header which maps the payload into memory based on its respective values.

In relation to above example, some similarities have been found in the loading process of shellcode, and the DLL file used to read the shellcode as well. Regarding the payload, various similarities have been confirmed with high confidence:
- Exception handling after the entry point
- Loading start functions for each plugin
- Plugin names
- Plugin information
- Structure of the malware configuration (offset of encrypted data)
- Hardcoded directories and a specific file name used for persistence

We have concluded that BloodAlchemy is highly likely to be a variant of Deed RAT, based on our deeply analysis and comparison results.
Summary
In this article, we have explained the analysis results of BloodAlchemy. The origin of BloodAlchemy and Deed RAT is ShadowPad and given the history of ShadowPad being utilized in numerous APT campaigns, it is crucial to pay special attention to the usage trend of this malware.
One more thing, our experts presented a talk titled "Into the Vapor to Tracking Down Unknown Panda's Claw Marks" at the Botconf 2024 held in Nice, France, discussing the analysis of BloodAlchemy.
The slide of presentation is available here, if you interested in the BloodAlchemy research, please check it.
Appendix
-
Disclosing the BLOODALCHEMY backdoor
https://www.elastic.co/security-labs/disclosing-the-bloodalchemy-backdoor↩ -
ShadowPad in corporate networks
https://securelist.com/ShadowPad-in-corporate-networks/81432/↩ -
ShadowPad
https://attack.mitre.org/software/S0596/↩ -
Space Pirates: a look into the group's unconventional techniques, new attack vectors, and tools
https://www.ptsecurity.com/ww-en/analytics/pt-esc-threat-intelligence/space-pirates-a-look-into-the-group-s-unconventional-techniques-new-attack-vectors-and-tools/↩